Learn more about dialysis and If you’re searching for the warning signs of kidney failure. Managing kidney health means becoming aware of supplementary effects of dialysis, pursuing other treatment alternatives, and making informed lifestyle decisions. Individuals can meet the challenges of kidney disease and increase the quality of their life by staying informed and working with their healthcare providers.
Recognize The Symptoms And Causes Of Kidney Failure
The signs and symptoms of fluid overload; electrolyte imbalance; removal of waste products; and red blood cell production will all present themselves when a kidney starts to fail. For example, the signs and symptoms of early kidney failure also look like signs and symptoms for other diseases as well, which can be confusing. If you have noticed these signs and symptoms and they do not resolve within a few days or you do not know what else may be causing them, please see your doctor. Particularly watch for the following symptoms:
- Loss of appetite
- General tiredness
- Headaches
- Itching with dry skin
- Nausea
- Weight loss (not on purpose)
Be Aware Of Later Signs Of Kidney Failure
Later signs and symptoms develop once kidney function has become much worse and the kidneys can no longer remove waste products from the blood. The signs of late kidney failure are:
- Changes in skin color
- Increasing sleepy or unable to concentrate and think clearly
- Muscle spasms and cramps
- Bone pain
- Numbness or swelling in hands and/or feet
- Bloody bowel movements
- Frequent hiccups
- Excessive thirst
- Female: Missing periods (amenorrhea)
- Sleeping changes
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic vomiting (especially in the morning)
The Symptoms Of End Stage Kidney Failure
End stage kidney failure happens when failure occurs as a result of damage to the kidneys. End Stage Renal Disease or ESRD is the last stage when your kidneys are not able to filter enough waste from your blood. By this point, your body will need kidney dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive. Diabetes and hypertension or high blood pressure are two of the leading causes of ESRD. Some other causes that can result in the possibility that you might develop ESRD are:
- Birth defects of the kidneys; e.g. polycystic kidney disease.
- Damage to the kidneys.
- Kidney stones and infections.
- Problems with arteries that supply blood to your kidneys.
- Certain medication for cancer, pain, etc. can damage your kidneys leading to kidney failure.
- Some chemicals – poisons.
- Autoimmune conditions; e.g. scleroderma; systemic lupus erythematosus; etc.
- Reflux – urine flowing back from the bladder to the kidneys damaging the kidneys.
Ask Your Doctor About Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis isn’t a complicated procedure with heavy machines; you can do this kind of dialysis from the comfort of your own home. You will need a surgeon to place a specific tube, called a catheter (or cath), into your peritoneal or abdominal cavity before you begin the peritoneal dialysis process. Using the catheter, you will be able to infuse a special dialysis fluid, known as dialysate. The solution absorbs waste from your bloodstream which is filtered through your abdomen by the dialysis process. There are two types of peritoneal dialysis; Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) and Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD).
With CAPD, you will infuse a little over two quarts of fluid into your abdomen via the abdominal catheter, twice a day. You will then “dwell” the fluid overnight, meaning the fluid will remain in your peritoneal cavity overnight. Then the fluid will need to be drained and discarded. Both the infusion and drainage will affect you as long as you have gravity on your side.
A device will cycle solution into your abdomen while you sleep. You will spend 30 minutes setting up the dialysis solution and machine prior to bed. In the morning, it will take about 10 minutes to take out the solution and disconnect everything. You will take the filters and return them every week to the dialysis center, where you will receive another set of filters for the next week. If looking for dialysis near you or dialysis in Delhi, you can contact carebox.
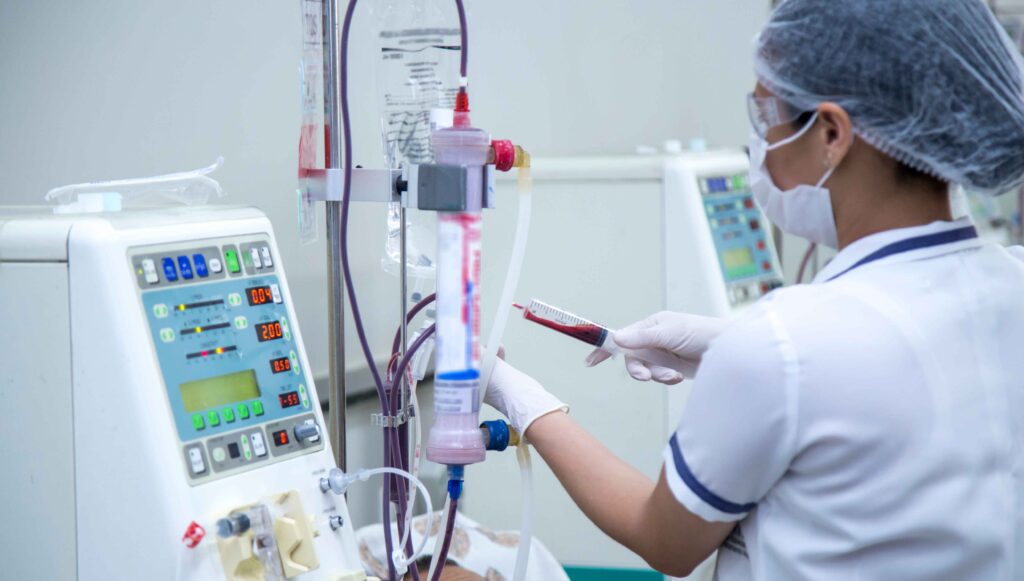
Go over hemodialysis with your doctor. Hemodialysis must be done in a hospital or dialysis center.
Hemodialysis uses special equipment to remove your blood from your body, filter the waste products, and return the blood to your body.
During hemodialysis, there are two filters involved. One removes waste products from your blood and the other filter is used to remove the fluid that has been used to rinse your blood. The filter in the machine is referred to in this case as an artificial kidney or dialyzer. Before your first dialysis, the surgeon will place an access port to your body. There are three types of access. A fistula is an access that is surgically made by connecting the artery and vein in the arm. This access gives you arterial, and venous blood to the machine. A graft could be used in combination with a catheter as in an access to connect an artery, and vein in the arm.
A catheter can be inserted in a large vein in your neck, if immediate access is needed during your recovery from acute kidney failure. A catheter is not permanent, but it can be useful while there is a need for immediate access.
There are two types of catheters. Non-tunneled catheters are temporary and can be placed easily in the neck (internal jugular vein) below the collar bone (subclavian vein) or in the groin (femoral vein). Tunneled catheters are tunneled subcutaneously and sub-fascia into the vein, below the collar bone, and can be used for long-term vascular access for dialysis in patients in whom a fistula or graft is not able to be made.
Conclusion
Being aware of the signs of renal failure is critical when it comes to early recognition and management of the problem. Consider asking yourself if you have had any of these symptoms: fatigue, loss of appetite, or skin changes in color, in which case it may be wise to consult your physician before your disease is well established.
There are some treatment options available (peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis) that can extend the lives of patients suffering from advanced renal failure. Dialysis can filter waste products from the body and may enhance the quality of life for the person undergoing this procedure.
You may be able to manage your kidney health effectively by partnering with your physician, understanding your health issues, and making some lifestyle changes. If you or a family member might be suffering from kidney problems, please do not hesitate to contact your local health care provider to discuss your treatment options and research next steps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. What is dialysis, and how does it function?
Dialysis is a treatment for people suffering from Kidney Failure. There are two basic types of Dialysis, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Both types are the same in that they filter waste and extra fluid from your blood just the same as your failing kidneys did.
Q. What is the cost of Dialysis?
Cost of dialysis ranges from 1000 to 6000 rs and more it depend to many factors.
Q. What are the two dialysis types?
Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis are the two types of dialysis.
Q. Is kidney dialysis painful?
No, generally not. You may feel a bit of discomfort when the injection is placed.
Q. What is the alarming stage of creatinine?
In the case of babies, high creatinine levels above 2.0 and in adults, 5.0 or more, may suggest severe loss of kidney function
Q. What is a normal albumin level?
The normal albumin level in adults is 3.4 to 5.4 grams per deciliter (g/dL).